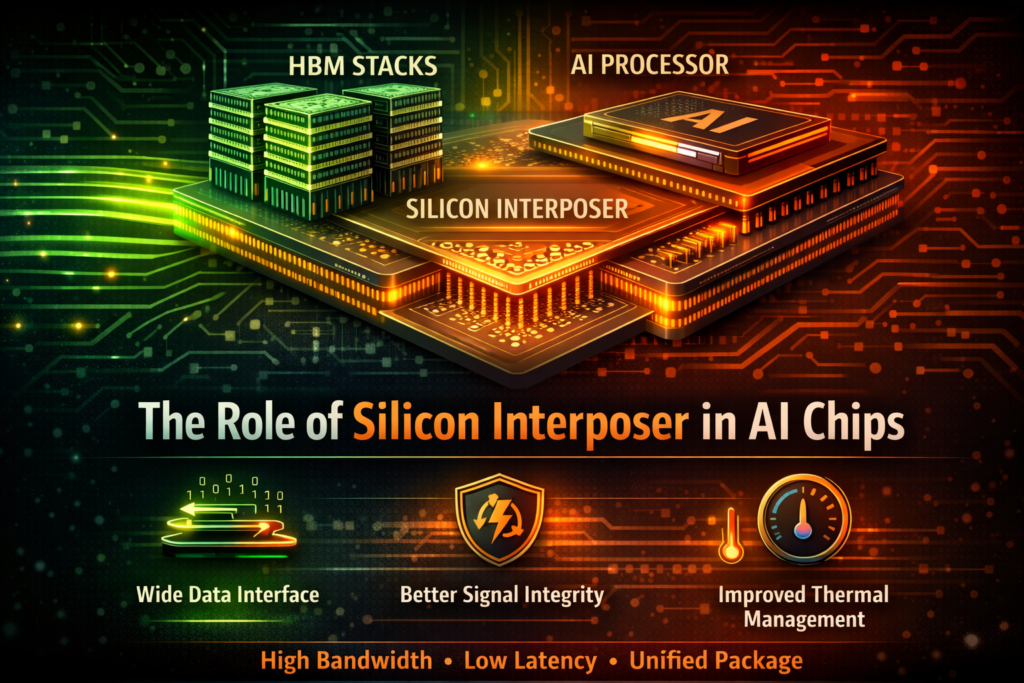
Introduction: The Hidden Layer Under AI Chips
Silicon interposer is the physical bridge that connects High Bandwidth Memory to AI processors, enabling ultra-wide data communication at scale.
When people talk about AI hardware, they usually mention GPUs, memory stacks, or bandwidth numbers. Almost no one talks about what physically connects them. Yet without that connection layer, HBM would not work the way it does.
Silicon interposers play a critical role in enabling high bandwidth memory to communicate efficiently with AI processors, forming a core part of modern AI memory architecture explained in detail in our guide to High Bandwidth Memory in AI.
That hidden layer is called the silicon interposer.
It does not compute. It does not store data. But it makes modern AI acceleration possible.
What Is a Silicon Interposer?
A silicon interposer is a thin layer of silicon that sits between the processor and memory, providing high-density wiring connections.
Unlike traditional PCB connections, which are relatively coarse, a silicon interposer allows extremely fine wiring density. This enables thousands of micro-connections between the AI chip and HBM stacks.
Think of it as a high-speed traffic exchange system. It allows massive amounts of data to move between memory and compute without signal loss or bottlenecks.
Without this layer, HBM could not deliver its full bandwidth potential.
Why HBM Needs a Silicon Interposer
HBM requires a silicon interposer because its bandwidth depends on extremely wide data interfaces that traditional packaging cannot support.
HBM uses thousands of parallel connections. A normal motherboard trace cannot handle that density. The silicon interposer solves this by:
- Providing ultra-fine wiring pitch
- Supporting wide memory buses
- Reducing electrical interference
- Shortening signal travel distance
This is what allows AI GPUs to sustain terabytes per second of memory bandwidth.
How Silicon Interposers Improve AI Performance
Silicon interposers improve AI performance by enabling higher bandwidth, lower latency, and improved signal integrity between memory and processors.
In AI workloads, thousands of compute cores request data simultaneously. If data paths are unstable or narrow, compute starvation occurs.
The interposer ensures:
- Stable high-speed signaling
- Lower power per bit transferred
- Reduced thermal stress
- Better scaling for future AI chips
In short, it allows HBM and GPUs to behave like a unified system instead of separate components.
Silicon Interposer vs Traditional Packaging
Traditional packaging relies on organic substrates and PCB routing, which limits bandwidth density.
Silicon interposers differ because they:
- Use fine lithography
- Support micro-bumps and TSV alignment
- Enable 2.5D chip integration
This packaging approach is often referred to as 2.5D integration, where logic and memory sit side-by-side on an interposer.
That structural change is why modern AI accelerators look physically different from older GPUs.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Silicon interposers increase manufacturing complexity because they require advanced lithography and precise alignment.
Yield issues can occur at multiple stages:
- TSV alignment
- Micro-bump bonding
- Interposer fabrication defects
Each added layer increases cost. This is one reason why HBM-based AI accelerators are expensive.
But without this complexity, AI performance at current scale would not exist.
Sustainability Implications
Silicon interposers contribute to AI hardware emissions due to additional fabrication steps and material usage.
Advanced packaging is energy-intensive. Interposer production adds wafer processing steps that increase carbon footprint.
While this improves runtime efficiency, the embodied emissions increase upfront manufacturing impact.
This makes interposers part of the broader sustainability debate in AI hardware.
The Future: Beyond Silicon Interposers?
Researchers are exploring alternatives such as:
- Advanced organic substrates
- Direct hybrid bonding
- 3D stacking without large interposers
Future AI hardware may reduce reliance on large interposer layers. However, for now, silicon interposers remain essential to high-performance AI systems.
Conclusion
Silicon interposers are the structural foundation that allows High Bandwidth Memory to connect to AI processors at extreme bandwidth levels.
They do not receive attention like GPUs or HBM stacks, but they are equally critical.
Without silicon interposers, modern AI accelerators would be limited by packaging constraints long before compute limits.
FAQs
A silicon interposer is a thin silicon layer that connects memory and processors using extremely dense wiring to enable high bandwidth communication.
AI chips need silicon interposers because HBM requires thousands of parallel connections that traditional packaging cannot support.
No. TSV connects layers vertically inside memory stacks, while the interposer connects memory stacks to the processor horizontally.
